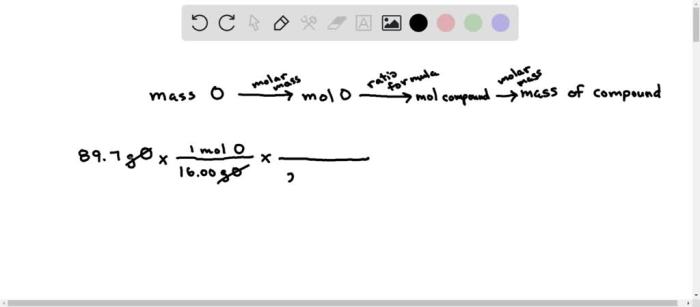
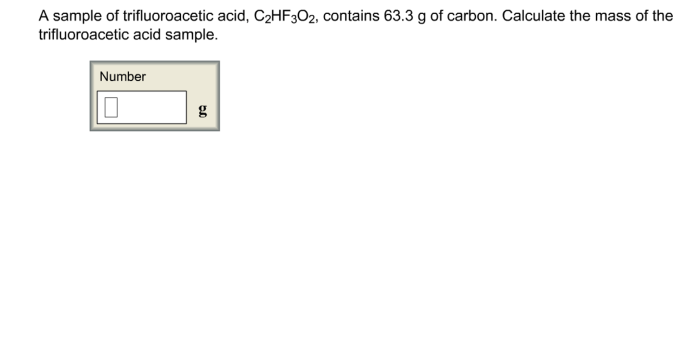
A sample of trifluoroacetic acid – Delving into the realm of chemistry, we embark on an exploration of trifluoroacetic acid, a versatile and widely used compound. With its unique properties and diverse applications, trifluoroacetic acid presents a captivating subject for scientific inquiry.
Trifluoroacetic acid, characterized by its molecular formula CF3COOH, is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. Its physical properties, including boiling point, melting point, density, and solubility, reflect its molecular structure and intermolecular interactions. As a strong acid, trifluoroacetic acid readily reacts with metals and forms salts, demonstrating its high reactivity.
Physical and Chemical Properties: A Sample Of Trifluoroacetic Acid

Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), with the molecular formula CF 3COOH, is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It has a molar mass of 114.02 g/mol and a chemical structure characterized by a trifluoromethyl group (-CF 3) bonded to a carboxylic acid group (-COOH).
Physical Properties
- Boiling point:72.4 °C
- Melting point:-15.3 °C
- Density:1.52 g/cm 3
- Solubility:Miscible with water and most organic solvents
Chemical Properties
- Acidity:TFA is a strong acid, with a pKa of 0.52. It is stronger than acetic acid but weaker than sulfuric acid.
- Reactivity with metals:TFA reacts with active metals, such as magnesium and zinc, to produce hydrogen gas and metal trifluoroacetates.
- Salt formation:TFA forms salts with bases, known as trifluoroacetates.
Synthesis and Production

Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is primarily synthesized through industrial processes involving the electrochemical fluorination of organic compounds. Laboratory-scale reactions can also produce TFA, but these methods are typically employed for research purposes or small-scale production.
Industrial Processes, A sample of trifluoroacetic acid
The primary industrial process for TFA synthesis involves the electrochemical fluorination of chlorodifluoromethane (HCFC-22) in the presence of hydrogen fluoride (HF). This reaction is carried out in a specialized electrochemical cell, where HCFC-22 is oxidized at the anode, leading to the formation of TFA and hydrogen gas.
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
HCFC-22 + 4 HF → 2 TFA + H2
The reaction conditions typically involve high temperatures and pressures, and the use of specific catalysts or promoters may enhance the efficiency of the process. The resulting TFA is then purified through distillation and other purification techniques to obtain the desired purity and quality.
Laboratory-Scale Reactions
In laboratory settings, TFA can be synthesized through various methods, including the hydrolysis of trifluoroacetyl chloride or the reaction of trifluoroacetic anhydride with water. These reactions are typically carried out under controlled conditions, using appropriate solvents and reaction parameters to optimize the yield and purity of the product.
- Hydrolysis of Trifluoroacetyl Chloride:This method involves the reaction of trifluoroacetyl chloride with water in the presence of a base, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The reaction proceeds through a nucleophilic substitution mechanism, resulting in the formation of TFA and the corresponding salt.
- Reaction of Trifluoroacetic Anhydride with Water:Trifluoroacetic anhydride can also be used to synthesize TFA through its reaction with water. This reaction involves the addition of water to the anhydride, leading to the formation of two molecules of TFA.
Applications and Uses

Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a versatile chemical with a wide range of applications in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, electronics, and organic chemistry.
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, TFA is commonly used as a solvent, reagent, and catalyst. Its strong acidity and ability to form hydrogen bonds make it an effective protonating agent and a catalyst for various reactions.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- TFA is used in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anti-cancer agents.
- It is also employed as a solvent for drug formulations, such as injections, nasal sprays, and eye drops.
Agrochemical Industry
- TFA is used as an intermediate in the production of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides.
- It is also used as a defoliant to remove leaves from plants before harvesting.
Electronics Industry
- TFA is used in the production of semiconductors and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
- It is also used as a cleaning agent in the manufacturing of electronic components.
Safety and Handling
Trifluoroacetic acid is a highly corrosive and toxic substance, requiring careful handling and storage to prevent accidents and exposure. Its vapors are irritating to the respiratory tract, eyes, and skin, while direct contact can cause severe burns. It is also flammable, presenting additional hazards during storage and handling.
To ensure safety, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) must be worn when handling trifluoroacetic acid. This includes chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, a lab coat, and a respirator if there is a risk of exposure to vapors. Proper ventilation is crucial to prevent the accumulation of toxic fumes in enclosed spaces.
Storage and Disposal
Trifluoroacetic acid should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area away from incompatible substances like strong bases and oxidizing agents. It must be kept in tightly sealed containers to prevent evaporation and contamination. Disposal should be carried out according to local regulations and guidelines, considering its corrosive and toxic nature.
Emergency Response
In case of an accidental spill or leak, evacuate the area immediately and alert emergency personnel. Neutralize the spill with a weak base like sodium bicarbonate or lime, and absorb the neutralized solution with an inert material like sand or vermiculite.
For skin contact, flush with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention immediately. In case of eye contact, flush with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention. If inhaled, move the person to fresh air and seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the safety precautions for handling trifluoroacetic acid?
Trifluoroacetic acid is corrosive and toxic, requiring careful handling. Proper personal protective equipment, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat, should be worn. Adequate ventilation is essential to avoid inhalation of vapors.
How is trifluoroacetic acid synthesized?
Trifluoroacetic acid can be synthesized through various methods, including the reaction of trifluoroacetic anhydride with water or the oxidation of 1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanol. Industrial processes typically employ these reactions on a larger scale.
What are the applications of trifluoroacetic acid in the pharmaceutical industry?
Trifluoroacetic acid is used as a reagent in the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and as a solvent for purification and crystallization processes. Its ability to form salts with basic compounds makes it valuable for API purification.