Kinetics and equilibrium regents questions delve into the fundamental principles that govern chemical reactions, providing a gateway to understanding the dynamic nature of chemical systems. This guide will equip you with a comprehensive overview of these concepts, empowering you to tackle regents questions with confidence.
From exploring the factors that influence reaction rates to harnessing equilibrium constants for predicting reaction outcomes, this guide will unravel the intricacies of chemical kinetics and equilibrium, illuminating their significance in diverse fields.
Kinetics and Equilibrium: Kinetics And Equilibrium Regents Questions
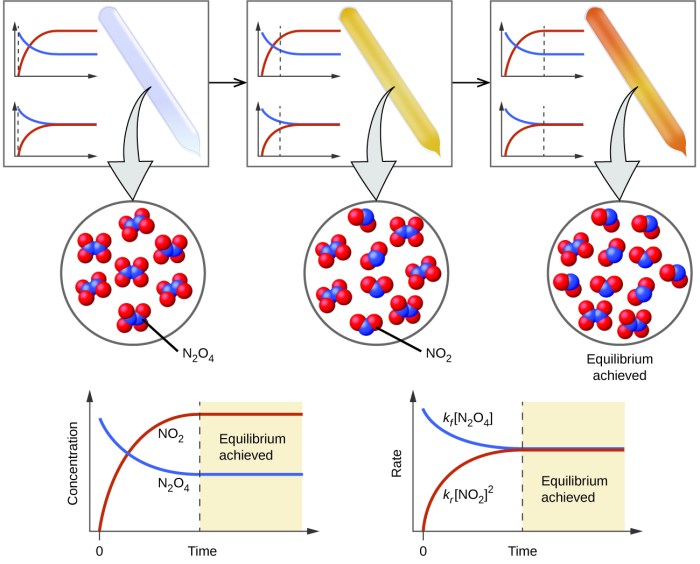
Chemical kinetics is the study of the rates of chemical reactions, while chemical equilibrium is the study of the conditions under which the concentrations of the reactants and products of a reaction do not change over time.
Kinetics and equilibrium are important concepts in chemistry because they allow us to understand and predict the behavior of chemical reactions. This knowledge is essential for a wide range of applications, including the design of new drugs, the development of new materials, and the understanding of environmental processes.
Factors Affecting Reaction Rates
- Concentration of the reactants: The rate of a reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of the reactants. This is because the more reactants there are, the more likely they are to collide with each other and react.
- Temperature: The rate of a reaction increases with increasing temperature. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the reactants have, and the more likely they are to have enough energy to overcome the activation energy barrier and react.
- Surface area of the reactants: The rate of a reaction increases with increasing surface area of the reactants. This is because the greater the surface area, the more reactants are exposed to each other and the more likely they are to collide and react.
- Catalysts: A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed. Catalysts work by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur, which has a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction.
Equilibrium Constants, Kinetics and equilibrium regents questions
An equilibrium constant is a number that expresses the relative amounts of reactants and products at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant is a constant for a given reaction at a given temperature.
Equilibrium constants can be used to predict the direction of a reaction. If the equilibrium constant is greater than 1, then the reaction will proceed to the right, forming more products. If the equilibrium constant is less than 1, then the reaction will proceed to the left, forming more reactants.
Equilibrium constants can also be used to solve equilibrium problems. For example, if we know the equilibrium constant for a reaction and the initial concentrations of the reactants, we can use the equilibrium constant to calculate the concentrations of the products at equilibrium.
Le Chatelier’s Principle
Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a change is made to the conditions of an equilibrium system, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the change.
Le Chatelier’s principle can be used to predict the effects of changes in conditions on equilibrium. For example, if we add more reactants to an equilibrium system, the system will shift to the right, forming more products. If we remove some products from an equilibrium system, the system will shift to the left, forming more reactants.
Le Chatelier’s principle can also be used to solve equilibrium problems. For example, if we know the equilibrium constant for a reaction and the initial concentrations of the reactants, we can use Le Chatelier’s principle to predict the direction of the reaction and the concentrations of the products at equilibrium.
Applications of Kinetics and Equilibrium
Kinetics and equilibrium are important concepts in a wide range of fields, including:
- Industry: Kinetics and equilibrium are used to design and optimize chemical processes. For example, kinetics is used to determine the rate of a reaction and the optimum temperature and pressure for the reaction. Equilibrium is used to predict the yield of a reaction and the composition of the products.
- Medicine: Kinetics and equilibrium are used to design and optimize drug delivery systems. For example, kinetics is used to determine the rate of release of a drug from a drug delivery system. Equilibrium is used to predict the concentration of a drug in the body over time.
- Environmental science: Kinetics and equilibrium are used to understand and predict the behavior of pollutants in the environment. For example, kinetics is used to determine the rate of degradation of a pollutant. Equilibrium is used to predict the distribution of a pollutant between different environmental compartments.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the key factors that affect reaction rates?
Temperature, concentration, surface area, and the presence of a catalyst.
How can equilibrium constants be used to predict the direction of a reaction?
If the equilibrium constant is greater than 1, the reaction will proceed in the forward direction. If it is less than 1, the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction.
What is Le Chatelier’s principle?
Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a change of condition is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the change.