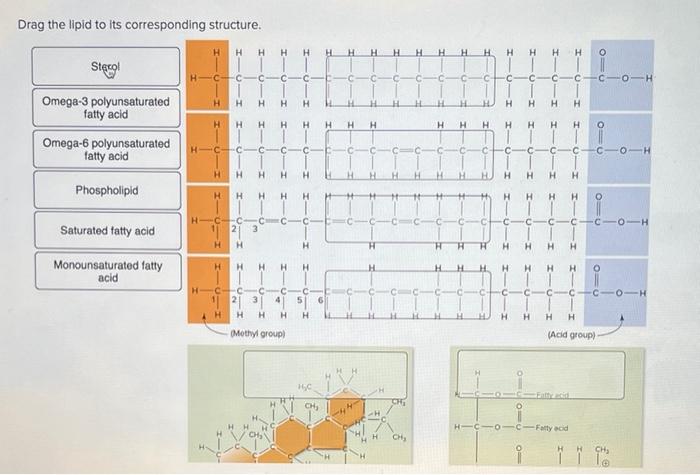
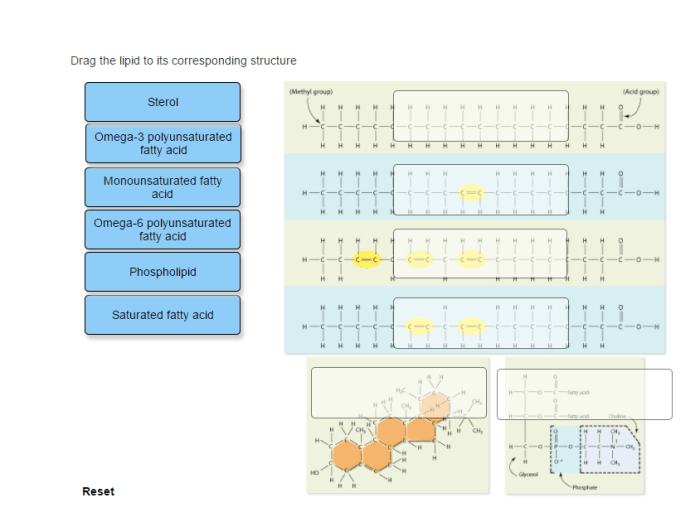
Drag the lipid name to its corresponding structure. Embark on an interactive journey to unravel the fascinating world of lipids, their diverse structures, and their crucial roles in biological systems.
Delve into the intricate details of lipid molecules, exploring their chemical composition, structural diversity, and the intimate relationship between their structure and function. Discover the different types of lipids, their unique properties, and their essential contributions to various biological processes.
Lipid Structure: Drag The Lipid Name To Its Corresponding Structure.
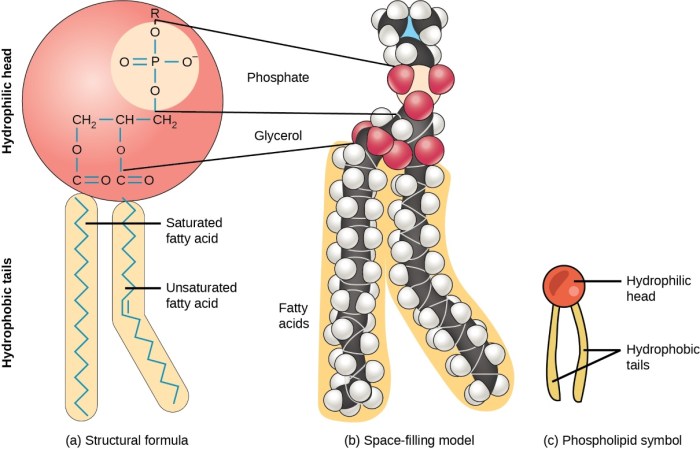
Lipid molecules generally consist of a glycerol backbone esterified with fatty acids. Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids, and the number and type of fatty acids attached to the glycerol backbone determine the specific type of lipid. The structure of a lipid molecule is closely related to its function.
Lipid Classification
- Simple lipids:Esters of fatty acids and glycerol or other alcohols.
- Compound lipids:Esters of fatty acids and glycerol or other alcohols, but also contain additional groups such as phosphate or nitrogen.
- Derived lipids:Lipids that are derived from simple or compound lipids by hydrolysis or other chemical reactions.
Lipid Properties
Lipids are generally hydrophobic, meaning they do not dissolve in water. This property is due to the presence of long, nonpolar hydrocarbon chains in their structure. Lipids are also amphipathic, meaning they have both hydrophilic (water-loving) and hydrophobic (water-hating) regions.
This property allows lipids to form micelles and liposomes, which are structures that can encapsulate water-soluble molecules.
Lipid Metabolism, Drag the lipid name to its corresponding structure.
Lipid metabolism is the process by which lipids are synthesized, broken down, and utilized for energy. Lipid metabolism is essential for many physiological processes, including energy storage, cell signaling, and hormone production.
Lipid Function
- Energy storage:Lipids are the body’s primary energy reserve. They are stored in adipose tissue and released into the bloodstream when needed for energy.
- Cell signaling:Lipids are involved in cell signaling pathways, and they can act as hormones or second messengers.
- Hormone production:Lipids are precursors to hormones such as estrogen and testosterone.
Questions Often Asked
What are lipids?
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They are essential components of cells and play crucial roles in energy storage, membrane formation, hormone production, and other biological processes.
What are the different types of lipids?
Lipids are classified into several types based on their structure and function, including fatty acids, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes.
What is the relationship between lipid structure and function?
The structure of a lipid molecule determines its function. For example, the long hydrocarbon chains of fatty acids make them ideal for energy storage, while the polar head groups of phospholipids enable them to form biological membranes.