ap us history dbq civil war transports readers to a transformative period in American history, inviting them to explore the complexities and consequences of the Civil War through an engaging narrative.
This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, key battles, and lasting impact of the conflict, shedding light on its profound influence on American society and the nation’s identity.
Overview of the American Civil War
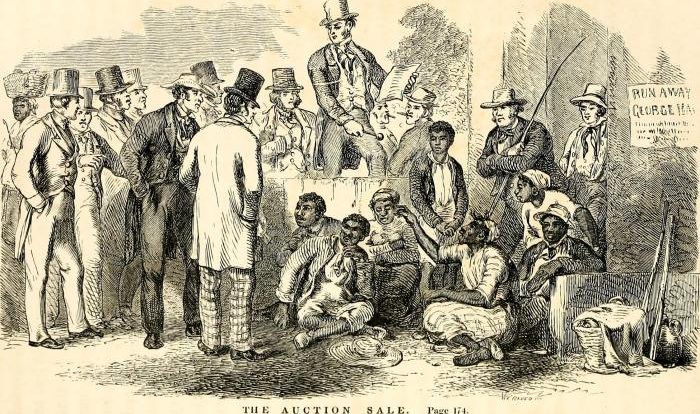
The American Civil War was a brutal conflict that pitted the Northern and Southern states against each other from 1861 to 1865. The war was fought over the issue of slavery, as the Southern states sought to preserve the institution, while the Northern states sought to abolish it.
Causes of the War
The American Civil War was caused by a number of factors, including:
- The issue of slavery
- The economic differences between the North and South
- The political differences between the North and South
Major Events of the War
The American Civil War was a long and bloody conflict, with major battles taking place at Gettysburg, Antietam, and Vicksburg. The war ended in 1865 with the surrender of the Confederate army.
Impact of the War, Ap us history dbq civil war
The American Civil War had a profound impact on American society. The war led to the abolition of slavery, the reunification of the country, and the establishment of a new national identity.
Causes of the Civil War

The Civil War, a conflict that tore the United States apart from 1861 to 1865, had deep-seated roots in a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors. At the heart of the conflict lay the issue of slavery, a divisive institution that shaped the nation’s identity and fueled growing tensions between the North and South.
Economic Factors
The economies of the North and South diverged significantly. The North embraced industrialization, with its factories and growing urban centers. In contrast, the South remained largely agricultural, reliant on large-scale plantations and the labor of enslaved people. This economic divide created a disparity in wealth and power, with the industrial North seeking to expand its economic influence and the agricultural South resisting any threat to its plantation-based economy.
Social Factors
Social differences between the North and South also contributed to the conflict. Northern society emphasized free labor, education, and social mobility. Southern society, on the other hand, was characterized by a rigid class system and a belief in the superiority of the white race.
These social differences led to growing resentment and distrust between the two regions.
Political Factors
Political disagreements further exacerbated the tensions between the North and South. The election of Abraham Lincoln, a Republican who opposed the expansion of slavery, in 1860 was seen as a direct threat to the South’s way of life. Southern states responded by seceding from the Union, leading to the outbreak of the Civil War.
The Role of Slavery
Slavery played a central role in the Civil War. The South’s economy was heavily dependent on the labor of enslaved people, and the institution of slavery was deeply ingrained in Southern society. The North, on the other hand, had a growing abolitionist movement that condemned slavery as a moral evil.
The conflict between these opposing views on slavery was a major catalyst for the war.
Different Perspectives on the Causes of the War
Historians have debated the relative importance of different factors in causing the Civil War. Some argue that economic factors were the primary driver, while others emphasize the role of social and political differences. The debate continues to this day, reflecting the complexity of the conflict and the enduring legacy of slavery in American history.
Key Battles and Turning Points
The American Civil War was marked by several pivotal battles and turning points that shaped its outcome. These confrontations not only tested the military prowess of both sides but also had profound political and social implications.
Major Battles
- Gettysburg (July 1-3, 1863):A three-day battle that ended in a Union victory and is considered the turning point of the war. The Confederate defeat shattered their hopes of invading the North and led to a shift in momentum in favor of the Union.
- Antietam (September 17, 1862):The bloodiest single-day battle in American history, resulting in a tactical draw but a strategic Union victory. President Lincoln used the battle to issue the Emancipation Proclamation, freeing slaves in Confederate-held territory.
- Vicksburg (May 18-July 4, 1863):A Union victory that gave the Union control of the Mississippi River and split the Confederacy in two, isolating Texas and Arkansas from the rest of the Confederate states.
Key Turning Points
- Emancipation Proclamation (January 1, 1863):President Lincoln’s declaration that all slaves in Confederate-held territory were free. It transformed the war into a moral crusade against slavery and helped galvanize support for the Union.
- Gettysburg Address (November 19, 1863):President Lincoln’s speech at the dedication of the Gettysburg National Cemetery, where he defined the war as a struggle for the preservation of the Union and the principles of equality and freedom.
- Surrender at Appomattox Court House (April 9, 1865):The formal surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee to Union General Ulysses S. Grant, effectively ending the war and marking the beginning of Reconstruction.
These battles and turning points were crucial in determining the outcome of the Civil War. They tested the limits of both sides and ultimately led to the preservation of the Union and the abolition of slavery.
Impact of the Civil War on American Society
The American Civil War had a profound impact on American society, shaping its social, economic, and political landscape for generations to come. It left an indelible mark on race relations and the future of the United States, and its legacy continues to influence American society today.
Social Consequences
The war had a devastating impact on American lives. An estimated 620,000 soldiers died, leaving countless families and communities shattered. The war also displaced millions of people, including freed slaves and refugees fleeing the fighting. The social fabric of the nation was torn apart, and the wounds of the war would take decades to heal.
Economic Consequences
The war had a profound economic impact on the United States. The North’s industrial economy boomed, while the South’s agricultural economy was devastated. The war also led to the creation of a national banking system and the expansion of the federal government’s role in the economy.
Political Consequences
The war had a profound impact on American politics. The victory of the Union preserved the United States as a single nation and strengthened the federal government. The war also led to the abolition of slavery and the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments to the Constitution, which granted citizenship and civil rights to African Americans.
Impact on Race Relations
The Civil War had a profound impact on race relations in the United States. The war led to the abolition of slavery, but it did not end racism. After the war, African Americans faced widespread discrimination and violence in the South.
For your upcoming AP US History DBQ on the Civil War, it’s crucial to understand the complexities of the era. While researching, consider supplementing your studies with resources like the AP Biology Unit 3 Test PDF for a comprehensive overview of the scientific advancements that shaped the period.
By incorporating diverse perspectives, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the causes and consequences of the Civil War, empowering you to craft a compelling historical analysis.
The legacy of slavery and racism continues to shape race relations in the United States today.
Legacy of the Civil War
The Civil War left a lasting legacy on American society. The war shaped the nation’s identity, its political system, and its economy. The war also had a profound impact on race relations and the struggle for civil rights. The legacy of the Civil War continues to influence American society today.
Primary Sources and Historical Interpretation: Ap Us History Dbq Civil War

Primary sources provide firsthand accounts of past events and are essential for understanding the Civil War. These sources include letters, diaries, speeches, newspapers, and government documents.
Historians use primary sources to interpret the past by analyzing their content and context. They consider the author’s perspective, biases, and purpose. By examining multiple primary sources, historians can triangulate information and develop a more comprehensive understanding of events.
Different Perspectives and Interpretations
The Civil War was a complex conflict with multiple perspectives. Historians have debated the causes, course, and consequences of the war for generations. Some interpretations focus on the economic and political factors that led to secession, while others emphasize the role of slavery and racial ideology.
No single interpretation of the Civil War is definitive. By examining a variety of primary sources and considering different perspectives, historians can gain a more nuanced understanding of this transformative event in American history.
Creating an Argument-Based Essay
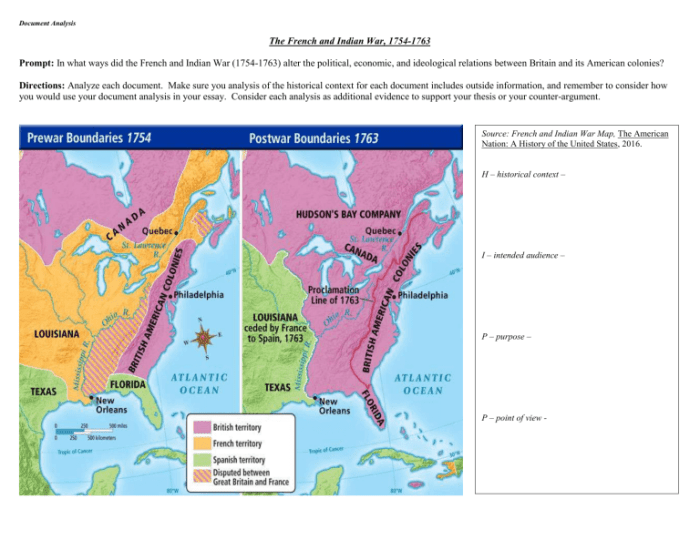
Constructing an effective argument-based essay on the Civil War entails organizing a persuasive piece around a central thesis statement supported by robust evidence from primary and secondary sources. This essay delves into the process of crafting such an essay, including identifying a clear thesis, gathering evidence, and addressing counterarguments.
Identifying a Clear Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement forms the backbone of an argument-based essay. It succinctly expresses the central claim or argument the essay aims to prove. To craft an effective thesis, consider the following:
- Specific and Focused:Avoid vague or overly broad statements. The thesis should precisely define the topic and the specific argument being made.
- Defensible:Ensure the thesis can be supported with evidence and logical reasoning. Avoid making claims that are too extreme or lack supporting evidence.
- Relevant:The thesis should directly address the prompt or topic assigned for the essay.
Gathering Evidence
To support the thesis, gather evidence from a variety of credible sources, including:
- Primary Sources:Original documents, such as letters, diaries, speeches, and newspaper articles, provide firsthand accounts of historical events.
- Secondary Sources:Books, articles, and documentaries provide interpretations and analyses of historical events based on primary source material.
When using evidence, accurately cite the source and consider its reliability and bias.
Anticipating and Addressing Counterarguments
Anticipate potential objections or counterarguments to your thesis and prepare responses to address them. This demonstrates a well-rounded understanding of the topic and strengthens the overall argument.
- Identify Potential Counterarguments:Consider opposing viewpoints and arguments that could challenge your thesis.
- Prepare Rebuttals:Develop logical and evidence-based responses to counterarguments, acknowledging the opposing view while providing a stronger argument in support of your thesis.
Writing a Historical Analysis Essay
Writing a historical analysis essay requires a systematic approach to organize and present your ideas. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you structure your essay effectively.
Identifying a Research Question and Thesis Statement
Begin by identifying a specific research question that you want to explore related to the Civil War. Your research question should be focused and narrow enough to allow for a thorough analysis. Once you have your research question, develop a clear thesis statement that answers the question and provides a roadmap for your essay.
Gathering and Evaluating Evidence
To support your thesis, you will need to gather evidence from both primary and secondary sources. Primary sources are firsthand accounts of events, such as letters, diaries, and speeches. Secondary sources are works written by historians or other scholars that interpret primary sources.
When evaluating sources, consider their credibility, relevance, and potential biases.
Constructing a Logical Argument
Organize your essay into paragraphs that each support a different aspect of your thesis. Use evidence from your sources to support your claims, and be sure to provide clear and logical reasoning to connect your evidence to your thesis. Avoid making unsupported generalizations or drawing conclusions that are not supported by the evidence.
Utilizing Historical Context
Understanding historical context is crucial for analyzing the Civil War. It provides a framework for interpreting events, decisions, and outcomes within their proper time and place.
For instance, comprehending the growing tensions between the North and South over slavery, economic disparities, and states’ rights helps explain the outbreak of the war. Similarly, knowing about the technological advancements and military strategies of the time allows us to appreciate the challenges and tactics involved in major battles.
Challenges and Limitations
However, using historical context also presents challenges. One is the risk of anachronism, or applying present-day values and perspectives to past events. Additionally, accessing reliable and unbiased sources can be difficult, as accounts from the time may be influenced by biases or limited knowledge.
Helpful Answers
What were the primary causes of the American Civil War?
Economic disparities, slavery, and political divisions played significant roles in fueling the conflict.
What were some of the key turning points in the war?
The battles of Gettysburg, Antietam, and Vicksburg proved decisive in shaping the outcome of the war.
How did the Civil War impact American society?
The war had profound consequences for race relations, the economy, and the nation’s political landscape.

