Welcome to the ultimate guide to Part B practice interpreting electrocardiograms answers, where we embark on a journey to decipher the intricate language of the heart. Understanding these answers is crucial for accurate patient care, and this guide will provide you with the knowledge and techniques to excel in ECG interpretation.
Throughout this comprehensive resource, we will delve into the significance of Part B in ECG interpretation, explore common pitfalls and errors, and uncover advanced techniques used in complex cases. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the confidence and skills to interpret ECGs like a seasoned professional.
Understanding Part B Practice Interpreting Electrocardiograms Answers
Part B of electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation exams assesses the candidate’s ability to interpret ECGs accurately. It involves analyzing and interpreting a series of ECG tracings to determine the underlying cardiac electrical activity and identify any abnormalities.
Part B practice questions typically present ECG tracings with varying degrees of complexity. Candidates are expected to identify and interpret the ECG components, including heart rate, rhythm, axis, intervals, and segments. Accurate interpretation is crucial for patient care as it helps clinicians diagnose cardiac conditions and guide appropriate treatment.
ECG Interpretation Techniques
Common ECG Interpretation Methods
- Measuring heart rate and rhythm
- Determining the electrical axis
- Analyzing intervals (PR, QRS, QT)
- Evaluating segments (ST, T)
These techniques allow clinicians to assess the electrical activity of the heart and identify potential abnormalities.
Normal and Abnormal ECG Patterns
Normal ECG patterns exhibit regular heart rate and rhythm, a normal electrical axis, and appropriate intervals and segments. Abnormal ECG patterns may indicate underlying cardiac conditions, such as arrhythmias, conduction disturbances, or myocardial ischemia.
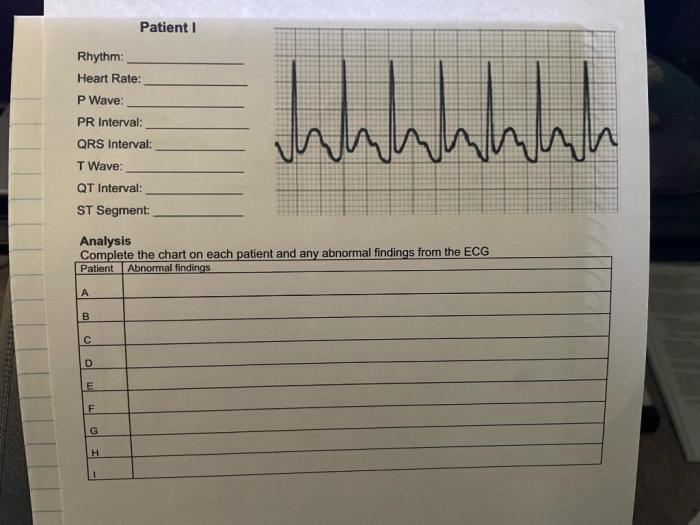
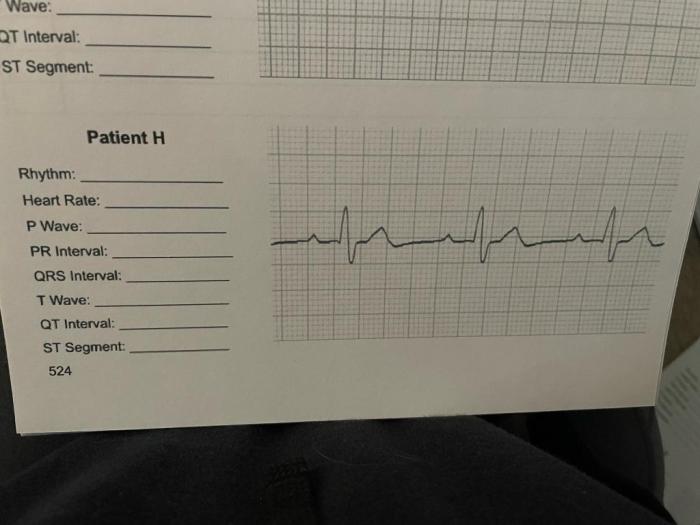
Practice Questions and Analysis: Part B Practice Interpreting Electrocardiograms Answers

Sample Part B Practice Questions, Part b practice interpreting electrocardiograms answers
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Identify the heart rate and rhythm. | Sinus rhythm, 75 bpm | Regular P waves preceding QRS complexes; PR interval within normal limits. |
| Determine the electrical axis. | +60 degrees | Positive QRS complex in lead I and negative QRS complex in lead aVF. |
Common Pitfalls and Errors
Pitfalls in ECG Interpretation
- Misinterpreting normal variants as abnormalities
- Overlooking subtle ECG changes
- Inaccurate measurement of intervals and segments
Avoiding Misinterpretations
To avoid misinterpretations, clinicians should:
- Be familiar with normal ECG patterns
- Consider the patient’s clinical presentation
- Use standardized criteria for ECG interpretation
Advanced Interpretation Techniques
Specialized ECG Interpretation Methods
- Vectorcardiography
- Signal averaging
- High-resolution ECG
These techniques provide additional information about cardiac electrical activity and enhance diagnostic accuracy in complex cases.
Quick FAQs
What is the significance of Part B in ECG interpretation?
Part B questions in ECG interpretation assess your ability to analyze and interpret real-world ECG tracings. Accurate interpretation is crucial for diagnosing cardiac conditions and guiding patient management.
How can I avoid common pitfalls and errors in ECG interpretation?
Understanding the limitations of ECGs, being aware of potential artifacts, and using a systematic approach to interpretation can help minimize errors. Consulting with experienced professionals and seeking continuing education can also enhance your accuracy.
What advanced techniques are used in ECG interpretation for complex cases?
Advanced techniques such as vectorcardiography, signal averaging, and high-resolution ECG can provide additional insights into complex ECG patterns. These techniques can aid in the diagnosis of subtle abnormalities and enhance the accuracy of interpretation.