The federal reserve decreases the money supply by 5 percent – As the Federal Reserve implements a 5 percent reduction in the money supply, this comprehensive analysis delves into its multifaceted implications and far-reaching impact. This detailed exploration unravels the intricate connections between monetary policy and economic variables, providing valuable insights for policymakers, financial professionals, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of macroeconomic dynamics.
The subsequent paragraphs will meticulously examine the effects of this monetary policy action on interest rates, inflation, economic growth, financial markets, foreign exchange rates, and its comparison to alternative tools. Additionally, potential risks and mitigation strategies will be thoroughly discussed, offering a comprehensive overview of this critical economic development.
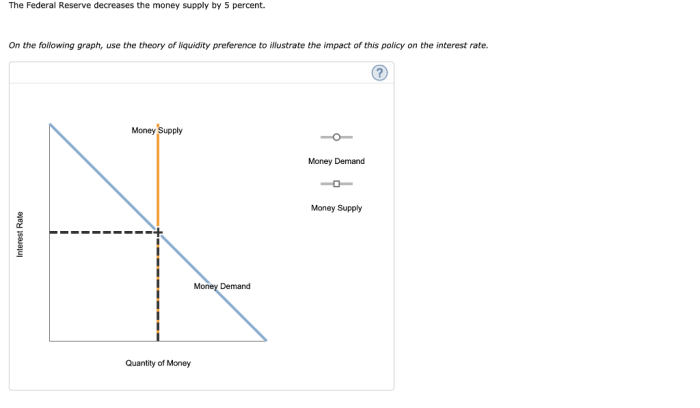
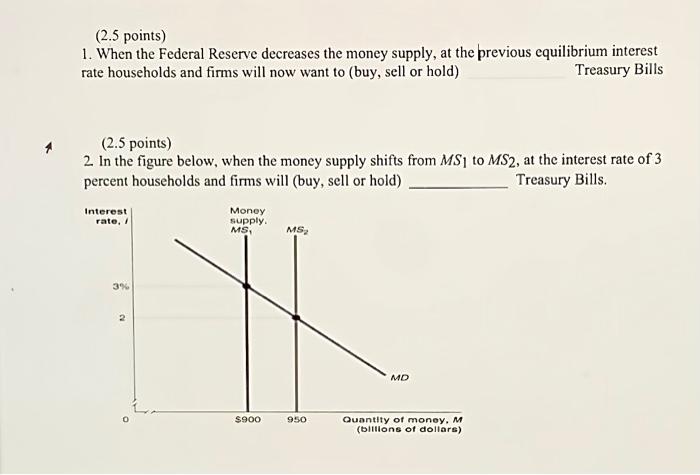
Impact on Interest Rates
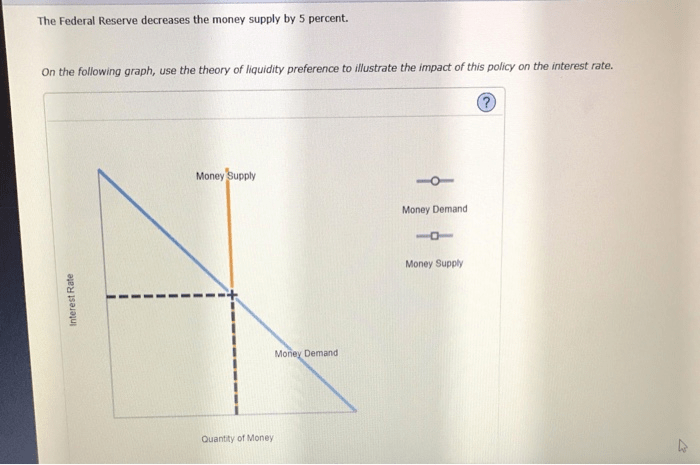
Decreasing the money supply by 5% may have a significant impact on interest rates, both in the short-term and long-term. In the short-term, the reduction in the money supply can lead to an increase in interest rates, as banks and other lenders have less money available to lend.
This can make it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money, which can slow down economic growth.
In the long-term, the impact of a 5% reduction in the money supply on interest rates is less clear. Some economists believe that it may lead to lower interest rates, as the reduced money supply can put downward pressure on inflation.
Lower inflation can make it easier for the central bank to lower interest rates without stimulating inflation.
Examples of Interest Rate Changes and their Impact on Borrowing and Lending Activities
- When interest rates increase, it becomes more expensive for businesses to borrow money to invest in new projects. This can lead to a decrease in investment and economic growth.
- When interest rates decrease, it becomes cheaper for businesses to borrow money to invest in new projects. This can lead to an increase in investment and economic growth.
- When interest rates increase, it becomes more expensive for consumers to borrow money to buy homes, cars, and other goods. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending and economic growth.
- When interest rates decrease, it becomes cheaper for consumers to borrow money to buy homes, cars, and other goods. This can lead to an increase in consumer spending and economic growth.
Effects on Inflation
A 5% reduction in the money supply can have a significant impact on inflation rates. In the short-term, the reduction in the money supply can lead to a decrease in inflation, as there is less money available to purchase goods and services.
This can be beneficial for consumers, as it can reduce the cost of living.
In the long-term, the impact of a 5% reduction in the money supply on inflation is less clear. Some economists believe that it may lead to higher inflation, as the reduced money supply can make it more difficult for businesses to produce goods and services.
This can lead to shortages of goods and services, which can drive up prices.
How Changes in the Money Supply Can Influence Price Levels and Consumer Spending, The federal reserve decreases the money supply by 5 percent
- When the money supply increases, there is more money available to purchase goods and services. This can lead to an increase in price levels, as businesses can charge more for their products.
- When the money supply decreases, there is less money available to purchase goods and services. This can lead to a decrease in price levels, as businesses must lower their prices to attract customers.
- When the money supply increases, consumers have more money to spend on goods and services. This can lead to an increase in consumer spending.
- When the money supply decreases, consumers have less money to spend on goods and services. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending.
Top FAQs: The Federal Reserve Decreases The Money Supply By 5 Percent
What is the primary objective of decreasing the money supply?
The primary objective is typically to combat inflation by reducing the amount of money in circulation, thereby making it more difficult to borrow and spend.
How does a decrease in the money supply affect economic growth?
A decrease in the money supply can potentially slow down economic growth by making it more expensive to borrow money for investment and consumption.
What are the potential risks associated with a significant decrease in the money supply?
Potential risks include deflation, reduced economic activity, and increased unemployment.