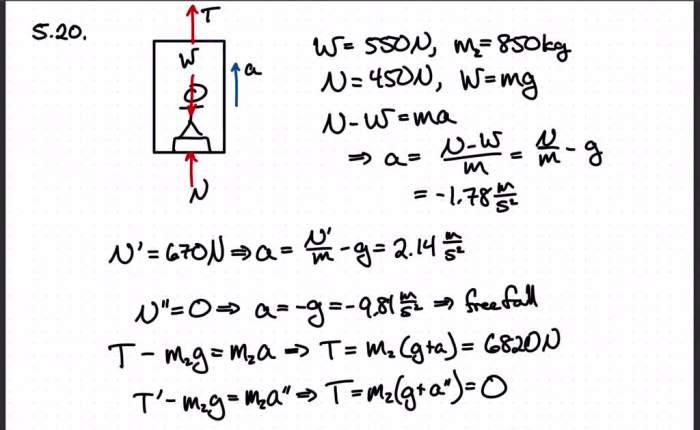
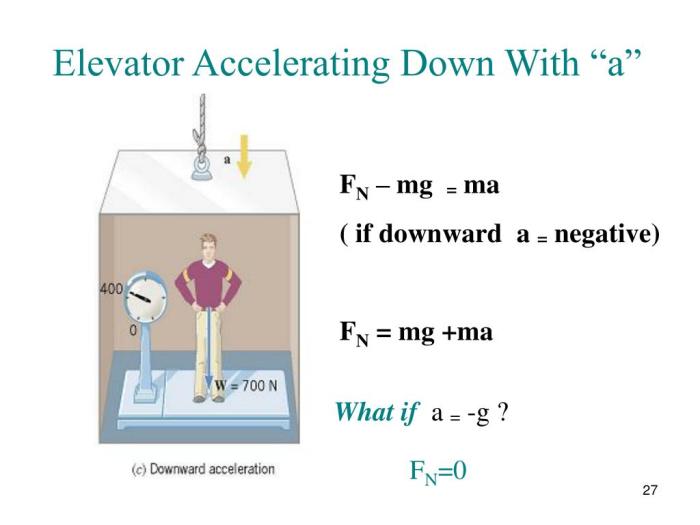
Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the elevator – Calculating the magnitude of elevator acceleration is a crucial aspect of understanding the motion of objects in accelerated frames of reference. This concept plays a significant role in various fields, including engineering, physics, and kinematics.
To determine the acceleration of an elevator, one can employ kinematic equations, motion analysis techniques, and the principles of force and acceleration.
Kinematic Equations
Kinematic equations are a set of equations that describe the motion of an object without considering the forces acting on it. They are used to calculate the acceleration of an object by relating its initial and final velocities, displacement, and time of motion.
Some commonly used kinematic equations include:
- v = u + at
- s = ut + 1/2 at 2
- v 2= u 2+ 2as
where:
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- t is the time of motion
- s is the displacement
These equations are particularly useful when the initial and final conditions of motion are known.
Motion Analysis: Calculate The Magnitude Of The Acceleration Of The Elevator

Motion analysis is the process of determining the motion of an object by observing its position, velocity, and acceleration over time. There are several methods for analyzing motion, including:
- Graphical analysis:This method involves plotting the object’s position, velocity, or acceleration against time. The slope of the graph represents the acceleration.
- Video analysis:This method uses video recordings to track the object’s motion. The software can then be used to calculate the object’s velocity and acceleration.
Each method has its own advantages and limitations. Graphical analysis is simple and inexpensive, but it can be less accurate than video analysis. Video analysis is more accurate, but it can be more time-consuming and expensive.
Free Fall and Projectile Motion
Free fall is the motion of an object falling under the influence of gravity alone. Projectile motion is the motion of an object thrown into the air, which is a combination of free fall and horizontal motion. Both free fall and projectile motion can be used to calculate acceleration.
In free fall, the acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity, which is approximately 9.8 m/s 2on Earth.
In projectile motion, the acceleration is the vector sum of the acceleration due to gravity and the acceleration due to the horizontal motion. The acceleration due to gravity is constant, while the acceleration due to the horizontal motion is zero.
Force and Acceleration
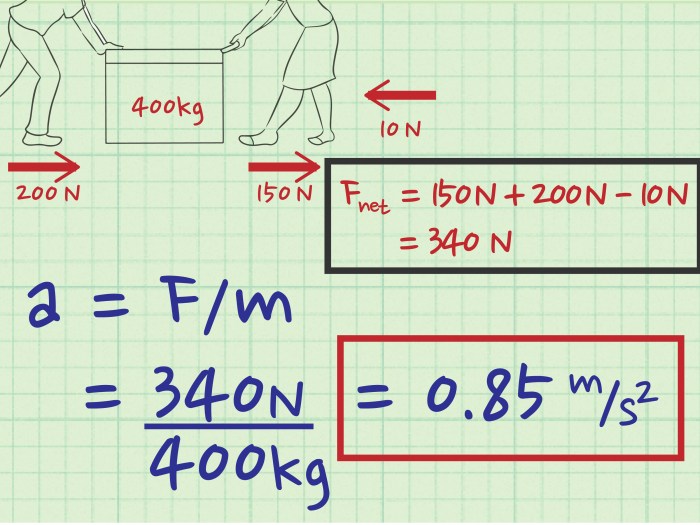
According to Newton’s second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
a = F/m
where:
- a is the acceleration
- F is the net force
- m is the mass
This equation shows that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied to it and inversely proportional to its mass. This means that a larger force will produce a greater acceleration, and a larger mass will produce a smaller acceleration.
Applications in Engineering and Physics
Acceleration calculations are used in a wide variety of applications in engineering and physics, including:
- Design:Engineers use acceleration calculations to design structures and machines that can withstand the forces acting on them.
- Testing:Engineers and physicists use acceleration calculations to test the performance of products and materials.
- Analysis:Engineers and physicists use acceleration calculations to analyze the motion of objects and to understand the forces acting on them.
In all of these applications, accuracy and precision in acceleration measurements are essential.
Key Questions Answered
What are the key factors that influence elevator acceleration?
Mass of the elevator, force applied by the motor, and air resistance are key factors.
How can motion analysis techniques be used to calculate elevator acceleration?
Graphical analysis of displacement-time graphs and video analysis of elevator motion can provide acceleration data.
What are some real-world applications of elevator acceleration calculations?
Elevator design, safety testing, and energy efficiency optimization rely on accurate acceleration calculations.