Function of a dissecting pins is an indispensable tool in scientific and laboratory settings, playing a pivotal role in various disciplines. From delicate dissections to precise manipulations, these unassuming instruments empower scientists to unravel the intricacies of life forms and advance our understanding of the natural world.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse functions, types, techniques, and applications of dissecting pins, providing a comprehensive resource for scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Functions of Dissecting Pins

Dissecting pins are indispensable tools in scientific and laboratory settings, serving various functions in dissections, specimen handling, and other intricate procedures. Their primary roles include:
- Specimen Positioning and Manipulation:Dissecting pins are used to gently hold and manipulate specimens during dissections or examinations. They provide a secure grip without damaging delicate tissues.
- Tissue Separation and Isolation:The sharp tips of dissecting pins allow researchers to carefully separate and isolate specific tissues or structures within a specimen.
- Labeling and Identification:Pins can be used to attach labels or markers to specimens for easy identification and tracking.
Examples of Use in Scientific Disciplines
Dissecting pins are widely employed in diverse scientific fields, including:
- Biology:In dissections of animals, plants, and microorganisms.
- Medicine:In surgical procedures, biopsies, and autopsies.
- Paleontology:In the study and preparation of fossils.
- Entomology:In the collection, preservation, and examination of insects.
- Botany:In the dissection and analysis of plant structures.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Precision:Sharp tips allow for precise manipulation and tissue separation.
- Versatility:Suitable for a wide range of specimens and procedures.
- Cost-effective:Relatively inexpensive compared to other laboratory tools.
Disadvantages:
- Damage Potential:Improper use can damage delicate specimens.
- Limited Holding Capacity:Not suitable for holding large or heavy specimens.
- Limited Versatility:May not be suitable for all types of dissections or procedures.
Types of Dissecting Pins

Dissecting pins are available in various types, each designed for specific applications. The key differences lie in their size, shape, and material.
Pin Sizes
- Small pins:Typically 2-3 cm in length, suitable for delicate dissections and handling small specimens.
- Medium pins:Around 4-5 cm in length, commonly used for general dissections and holding specimens in place.
- Large pins:Up to 10 cm in length, ideal for securing larger specimens or holding down tissues during dissection.
Pin Shapes
- Straight pins:General-purpose pins with a straight shaft, suitable for pinning specimens in various orientations.
- T-pins:T-shaped pins with a crossbar at the top, providing additional stability when securing specimens.
- Curved pins:Pins with a curved shaft, useful for holding specimens at specific angles or reaching into confined spaces.
Pin Materials
- Stainless steel:Corrosion-resistant and durable, suitable for most dissection applications.
- Nickel-plated:Similar to stainless steel but provides a slightly sharper point for more precise dissections.
- Plastic:Lightweight and non-conductive, suitable for handling delicate specimens or electrical applications.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Small Pins | Medium Pins | Large Pins |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 2-3 cm | 4-5 cm | Up to 10 cm |
| Shape | Straight, T-pins, Curved | Straight, T-pins | Straight |
| Material | Stainless steel, Nickel-plated | Stainless steel, Nickel-plated | Stainless steel |
| Application | Delicate dissections | General dissections | Larger specimens |
Techniques for Using Dissecting Pins

Dissecting pins are versatile tools that require proper handling to ensure safety and effectiveness. This section will guide you through the techniques for using dissecting pins, including insertion, removal, and manipulation in various biological specimens.
Inserting Dissecting Pins
- Grasp the pin firmly with forceps near the head.
- Position the pin perpendicular to the specimen surface.
- Apply gentle pressure to insert the pin, ensuring it penetrates to the desired depth.
Removing Dissecting Pins
- Use forceps to grasp the pin close to the specimen.
- Apply gentle upward pressure to lift the pin out of the specimen.
- Avoid pulling or twisting the pin, as this can damage the specimen.
Manipulating Dissecting Pins
- To rotate the specimen, hold the pin with forceps and gently move it in a circular motion.
- To lift or hold the specimen, insert two pins into the specimen and gently lift or manipulate it as needed.
- To secure the specimen to a surface, insert pins into the specimen and press them into a wax or clay base.
Care and Maintenance of Dissecting Pins: Function Of A Dissecting Pins

Dissecting pins are delicate tools that require proper care and maintenance to ensure their longevity and effectiveness. Neglecting their upkeep can lead to contamination, damage, and reduced functionality, hindering your dissection work.
To maintain the integrity of your dissecting pins, follow these essential guidelines:
Cleaning and Sterilization
- After each use, thoroughly clean your dissecting pins using soap and water. This removes any organic matter or debris that may harbor bacteria or compromise their sharpness.
- For sterilization, immerse the pins in a disinfectant solution, such as 70% ethanol or bleach, for a specified duration. This kills microorganisms that could contaminate your specimens or cause infections.
Storage
- Store your dissecting pins in a dry, protected location, away from moisture and extreme temperatures. Moisture can cause rust and damage the pins, while extreme temperatures can alter their temper and sharpness.
- Consider using a pincushion or magnetic strip to keep your pins organized and prevent them from bending or losing their points.
Extending Lifespan
- Avoid using dissecting pins for tasks that could damage them, such as prying or cutting. Use appropriate tools for such tasks.
- Handle the pins with care, avoiding dropping or mishandling them, as this can cause bending or breakage.
- Sharpen your dissecting pins regularly using a sharpening stone or sandpaper to maintain their sharpness and precision.
Applications in Different Fields
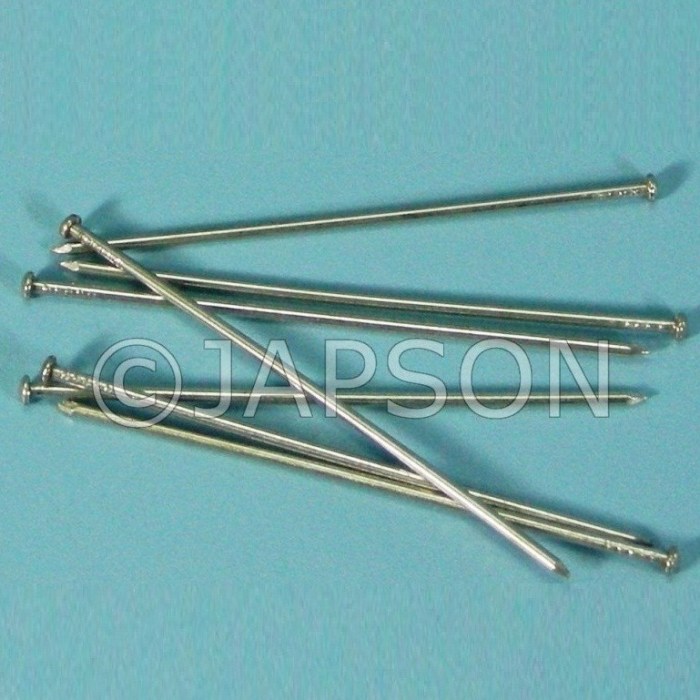
Dissecting pins, seemingly simple tools, find extensive applications across various scientific disciplines. Their versatility and precision make them indispensable for intricate tasks and delicate procedures.
Biology
In biology, dissecting pins serve as essential tools for dissecting and examining specimens. They aid in holding tissues and organs in place, allowing scientists to study their structure and relationships. Moreover, pins facilitate the collection and preservation of biological samples, ensuring their integrity for further analysis.
Zoology
Zoologists utilize dissecting pins to examine animal specimens, ranging from insects to large mammals. They are particularly valuable in entomological studies, where pins help preserve and display insect collections. The use of pins allows for detailed observation of external and internal structures, contributing to the classification and identification of insect species.
Botany
In botany, dissecting pins assist in the dissection and study of plant tissues and structures. They facilitate the examination of plant anatomy, including the arrangement of cells, tissues, and organs. Additionally, pins are used to mount and preserve plant specimens for further analysis and reference.
Entomology
Entomologists heavily rely on dissecting pins for preserving and displaying insect specimens. The pins ensure proper alignment and positioning of insects, allowing for detailed observation and study. They also facilitate the creation of insect collections for research, education, and museum exhibitions.
Dissecting pins are essential tools for holding specimens in place during dissection. They come in a variety of sizes and shapes, depending on the type of specimen being dissected. For instance, when tackling algebra problems, you may find yourself stumped.
In such cases, the envision algebra 1 answer key can provide valuable guidance. However, returning to our discussion of dissecting pins, their sharp points allow them to easily penetrate tissue, while their blunt ends prevent them from damaging the specimen.
Illustrations and Visual Aids

To enhance the understanding of dissecting pins, various visual aids can be employed.
These visual aids can help provide a clear and comprehensive representation of the functions and applications of dissecting pins.
Clear and Detailed Illustrations or Images
Detailed illustrations or images of dissecting pins in use can be valuable for demonstrating the proper handling and techniques.
- These illustrations can depict the pins being used for holding specimens, dissecting tissues, or manipulating delicate structures.
- By providing a visual representation, learners can better understand the functionality and versatility of dissecting pins.
Table or Infographic Summarizing Key Functions and Applications
A table or infographic can effectively summarize the key functions and applications of dissecting pins.
- This visual aid can provide a concise overview of the various uses of dissecting pins in different fields.
- By organizing the information in a clear and structured manner, learners can quickly grasp the diverse applications of these essential laboratory tools.
Video Demonstrating Proper Techniques, Function of a dissecting pins
A video demonstration can be highly effective in showcasing the proper techniques for using dissecting pins in a laboratory setting.
- The video can provide step-by-step instructions on how to handle, insert, and manipulate dissecting pins.
- By observing the techniques demonstrated in the video, learners can gain a practical understanding of the proper use of dissecting pins.
Detailed FAQs
What are the primary functions of dissecting pins?
Dissecting pins serve as precise tools for holding, manipulating, and dissecting biological specimens during scientific investigations.
What are the different types of dissecting pins available?
Dissecting pins come in various sizes, shapes, and materials, each suited for specific applications, such as straight pins, T-pins, and insect pins.
How should dissecting pins be properly used?
Handle dissecting pins with care, insert them perpendicularly into specimens, and use appropriate force to avoid damage.
How can dissecting pins be maintained for optimal performance?
Clean and sterilize dissecting pins regularly to prevent contamination, store them in a dry place, and avoid bending or overusing them.